|
The GAia Map of the Brightness Of Natural SkyAbout GAMBONS |
Return to GAMBONS |
|---|
We are working in a new version of Gambons web, with more funcionalities. This new web is expected to be ready by mid-2023.
What is GAMBONS?
GAMBONS (GAia Map of the Brightness Of the Natural Sky) is a model of the natural night brightness of the sky in cloudless and moonless nights. GAMBONS is based on the extra-atmospheric star radiance obtained from the Gaia catalogue. For the brightest stars, not included in Gaia-DR3, we have used the Hipparcos catalogue instead. After adding up to the star radiance the contributions of the diffuse galactic and extragalactic light, zodiacal light and airglow, and taking into account the effects of atmospheric attenuation and scattering, the radiance detected by ground-based observers is estimated. At the moment, GAMBONS does not include the Moon and Sun contributions.The citation for GAMBONS is Masana et al. 2020 (MNRAS 501, 5443-5456). Download the paper here.
The current version of GAMBONS is described in this other paper.
Running GAMBONS
- Select a location and date.
- Set the airglow and atmospheric parameters:
- Airglow spectrum: the default airglow spectrum is computed from the ESO SkyCalc web page, with a Monthly Averaged Solar Radio Flux equal to 100 sfu.
Values of Solar Radio Flux can be obtained from the Canadian Space Weather Forecast Centre (CSWFC).
Other spectra computed from ESO SkyCalc could be used, if calculated for the Cerro Paranal altitude (2640 m above the sea level) in the wavelength range from 350 nm to 1050 nm.
- Airglow value: a scale factor for the airglow radiance (%).
- The aerosol optical thickness (wavelength dependent) is modelled by:
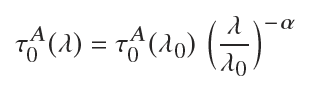
where α is the socalled Ångstrom exponent, and τ0(λ0) is the aerosol optical thickness of the whole atmosphere, measured along a vertical path, for the reference wavelength λ0=550nm. Both parameters can be set.
- Run the model by clicking the "Compute" button and download the data, if you wish.
- The output file contains the azimuth (°), the altitude (°) and the mag arcsec-2 for each HealPix in the map.
- Some additional values are shown when the map is generated:
- Zenith magnitude (mag·arcsec-2): average magnitude of the circular sky region (radi=5°) around the zenith.
- Horizontal irradiance (W·m-2): the total amount of radiation, per unit area, received from above by a horizontal surface:
- Average upper hemisphere radiance (W·m-2·sr-1): obtained by directly averaging the equal-solid angle HealPix radiance across the upper hemisphere. The same for the photopic and scotopic luminances, in cd·m-2.
- Average full sphere radiance (W·m-2·sr-1): the average of the radiance calculated taking into account not only the upper hemisphere above the observer but also the light from the sky reflected by the ground (the 'lower hemisphere'). To simplify, we assume the ground reflects light in a Lambertial way, with the in-band terrain reflectance ρ=0.2.

with Δi the HealPix solid angle element (sr).
For the human photopic and scotopic bands, E is multiplied by 683 lm/W or 1700 lm/W, respectively, to get the corresponding Horizontal illuminances (lx).
Scattering model
In this web version the scattering is computed in a simpler, but less accurate, way than the full scattering model described in the paper. It consists in replacing τ0(λ) by an effective optical depth τ0(λ)eff = γ τ0(λ), (see Duriscoe D. M., 2013, PASP, 125, 1370), with a value of γ=0.5. The results obtained with this simplified scattering model could differ from the results get with the full model. At zenith, the simplified model tends to be darker (compared with the full model) in around 0.075 - 0.1 mag arcsec-2, whereas near the horizon it is brighter in 0.1 - 0.2 mag arcsec-2. The implementation of the full model is not feasible in this version due to the CPU time needed. If more accurate results are required, contact whit us.
Photometric systems
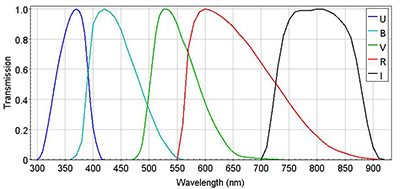
The currently available photometric bands in GAMBONS are:Johnson-Cousins system (UBVRI)
The UBVRI magnitudes are defined in the Vega system. The fluxes in those bands correspond to filters with transmission peak equal to 1.
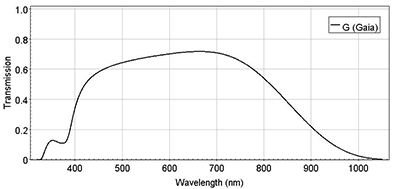
Gaia filter (G)
The Gaia magnitude is defined in the Vega system. Note that the filter's transmission is not normalized to 1.
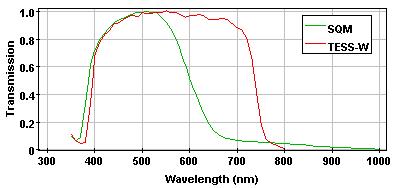
SQM and TESS-W bands
SQM and TESS-W bands are defined in the AB system. The magnitude shown in the map is derived from the integrated radiance in the band without take into account the PSF of the instrument. However, the PSF is considered in the computation of the zenith magnitude.
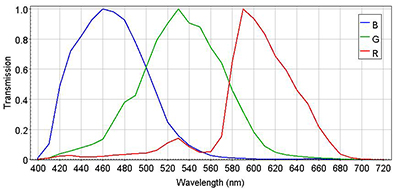
RGB System
The RGB magnitudes are defined in the AB system. The fluxes in those bands correspond to filters with transmission peak equal to 1
Human vision (photopic and scotopic)
Photopic and scotopic magnitudes are defined in the Vega system.
Sloan system (ugriz)
The Sloan magnitudes are defined in the AB system. Note that the filter transmission are not normalized.
Contact
Contact addresses: emasana at fqa.ub.edu (E. Masana; astrophysical sources, website), salva.bara at usc.gal (S. Bará; atmospheric modeling).